Events
OpenOffice.org dialogs and forms are based on an event-oriented programming model where you can assign event handlers to the control elements. An event handler runs a predefined procedure when a particular action occurs. You can also edit documents or open databases with event handling as well as access other control elements.
OpenOffice.org control elements recognize different types of events that can be triggered in different situations. These event types can be divided into four groups:
- Mouse control: Events that correspond to mouse actions (for example, simple mouse movements or a click on a particular screen location).
- Keyboard control: Events that are triggered by keyboard strokes.
- Focus modification: Events that OpenOffice.org performs when control elements are activated or deactivated.
- Control element-specific events: Events that only occur in relation to certain control elements.
When you work with events, make sure that you create the associated dialog in the OpenOffice.org development environment and that it contains the required control elements or documents (if you apply the events to a form).
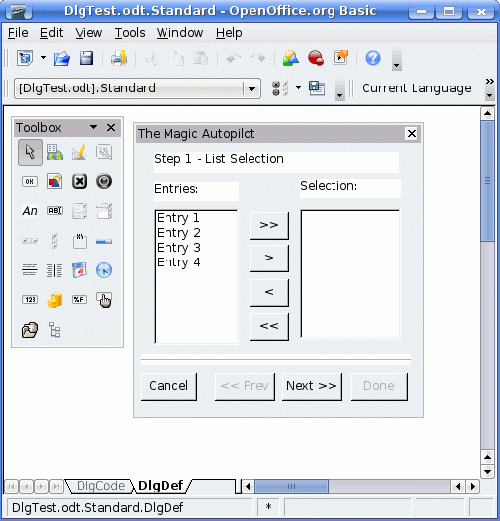
The figure above shows the OpenOffice.org Basic development environment with a dialog window that contains two list boxes. You can move the data from one list to the other using the buttons between the two list boxes.
If you want to display the layout on screen, then you should create the associated OpenOffice.org Basic procedures so that they can be called up by the event handlers. Even though you can use these procedures in any module, it is best to limit their use to two modules. To make your code easier to read, you should assign meaningful names to these procedures. Jumping directly to a general program procedure from a macro can result in unclear code. Instead, to simplify code maintenance and troubleshooting, you should create another procedure to serve as an entry point for event handling - even if it only executes a single call to the target procedure.
The code in the following example moves an entry from the left to the right list box of a dialog.
Sub cmdSelect_Initiated
Dim lstEntries As Object
Dim lstSelection As Object
lstEntries = Dlg.getControl("lstEntries")
lstSelection = Dlg.getControl("lstSelection")
If lstEntries.SelectedItem > 0 Then
lstSelection.AddItem(lstEntries.SelectedItem, 0)
lstEntries.removeItems(lstEntries.SelectItemPos, 1)
Else
Beep
End If
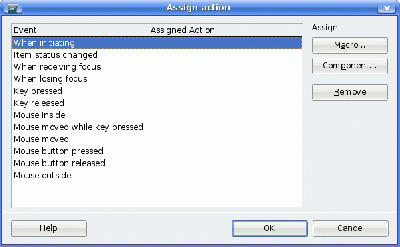
End SubIf this procedure was created in OpenOffice.org Basic, you can assign it to an event required using the property window of the dialog editor.
The Assign Action dialog lists all of the available Events. To assign a macro to an event:
- Select the event
- Click Macro...
- Browse to and select the macro you want to assign
- Click OK
Parameters
The occurrence of a particular event is not always enough for an appropriate response. Additional information may be required. For example, to process a mouse click, you may need the screen position where the mouse button was pressed.
In OpenOffice.org Basic, you can use object parameters to provide more information about an event to a procedure, for example:
Sub ProcessEvent(Event As Object)
End SubThe structure and properties of the Event object depend on the type of event that triggers the procedure call.
Regardless of the type of event, all objects provide access to the relevant control element and its model. The control element can be reached using Event.Source and its model using Event.Source.Model.
You can use these properties to trigger an event within an event handler.
Mouse Events
OpenOffice.org Basic recognizes the following mouse events:
- Mouse moved
- user moves mouse
- Mouse moved while key pressed
- user drags mouse while holding down a key
- Mouse button pressed
- user presses a mouse button
- Mouse button released
- user releases a mouse button
- Mouse outside
- user moves mouse outside of the current window
The structure of the associated event objects is defined in the com.sun.star.awt.MouseEvent structure which provides the following information:
- Buttons (short)
- button pressed (one or more constants in accordance with com.sun.star.awt.MouseButton)
- X (long)
- X-coordinate of mouse, measured in pixels from the top left corner of the control element
- Y (long)
- Y-coordinate of mouse, measured in pixels from the top left corner of the control element
- ClickCount (long)
- number of clicks associated with the mouse event (if OpenOffice.org can respond fast enough, ClickCount is also 1 for a double-click because only an individual event is initiated)
The constants defined in com.sun.star.awt.MouseButton for the mouse buttons are:
- LEFT
- left mouse button
- RIGHT
- right mouse button
- MIDDLE
- middle mouse button
The following example outputs the mouse position as well as the mouse button that was pressed:
Sub MouseUp(Event As Object)
Dim Msg As String
Msg = "Keys: "
If Event.Buttons AND com.sun.star.awt.MouseButton.LEFT Then
Msg = Msg & "LEFT "
End If
If Event.Buttons AND com.sun.star.awt.MouseButton.RIGHT Then
Msg = Msg & "RIGHT "
End If
If Event.Buttons AND com.sun.star.awt.MouseButton.MIDDLE Then
Msg = Msg & "MIDDLE "
End If
Msg = Msg & Chr(13) & "Position: "
Msg = Msg & Event.X & "/" & Event.Y
MsgBox Msg
End Sub
Keyboard Events
The following keyboard events are available in OpenOffice.org Basic:
- Key pressed
- user presses a key.
- Key released
- user releases a key
Both events relate to logical key actions and not to physical actions. If the user presses several keys to output a single character (for example, to add an accent to a character), then OpenOffice.org Basic only creates one event.
A single key action on a modification key, such as the Shift key or the Alt key does not create an independent event.
Information about a pressed key is provided by the event object that OpenOffice.org Basic supplies to the procedure for event handling. It contains the following properties:
- KeyCode (short)
- code of the pressed key (default values in accordance with com.sun.star.awt.Key)
- KeyChar (String)
- character that is entered (taking the modification keys into consideration)
The following example uses the KeyCode property to establish if the Enter key, the Tab key, or one of the other control keys has been pressed. If one of these keys has been pressed, the name of the key is returned, otherwise the character that was typed is returned:
Sub KeyPressed(Event As Object)
Dim Msg As String
Select Case Event.KeyCode
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.RETURN
Msg = "Return pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.TAB
Msg = "Tab pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.DELETE
Msg = "Delete pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.ESCAPE
Msg = "Escape pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.DOWN
Msg = "Down pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.UP
Msg = "Up pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.LEFT
Msg = "Left pressed"
Case com.sun.star.awt.Key.RIGHT
Msg = "Right pressed"
Case Else
Msg = "Character " & Event.KeyChar & " entered"
End Select
MsgBox Msg
End SubInformation about other keyboard constants can be found in the API Reference under the com.sun.star.awt.Key group of constants.
Focus Events
Focus events indicate if a control element receives or loses focus. You can use these events to, for example, determine if a user has finished processing a control element so that you can update other elements of a dialog. The following focus events are available:
- When receiving focus
- element receives focus
- When losing focus
- element loses focus
The Event objects for the focus events are structured as follows:
- FocusFlags (short)
- cause of focus change (default value in accordance with com.sun.star.awt.FocusChangeReason )
- NextFocus (Object)
- object that receives focus (only for the When losing focus event)
- Temporary (Boolean)
- the focus is temporarily lost
Control Element-Specific Events
In addition to the preceding events, which are supported by all control elements, there are also some control element-specific events that are only defined for certain control elements. The most important of these events are:
- When Item Changed
- the value of a control element changes
- Item Status Changed
- the status of a control element changes
- Text modified
- the text of a control element changes
- When initiating
- an action that can be performed when the control element is triggered (for example, a button is pressed)
When you work with events, note that some events, such as the When initiating event, can be initiated each time you click the mouse on some control elements (for example, on radio buttons). No action is performed to check if the status of the control element has actually changed. To avoid such “blind events”, save the old control element value in a global variable, and then check to see if the value has changed when an event is executing.
The When initiating event is also noteworthy for the following reasons:
- This event is initiated by either a key-press or a mouse button. Thus, it provides a consistent interface for users who navigate by mouse or by keyboard.
- When the Repeat property of a command button is set to True, this event is the one which is repeatedly sent, as long as the triggering action (key down or mouse-button down) remains in effect.
The properties for the Item Status Changed event are:
- Selected (long)
- currently selected entry
- Highlighted (long)
- currently highlighted entry
- ItemId (long)
- ID of entry
| Content on this page is licensed under the Public Documentation License (PDL). |